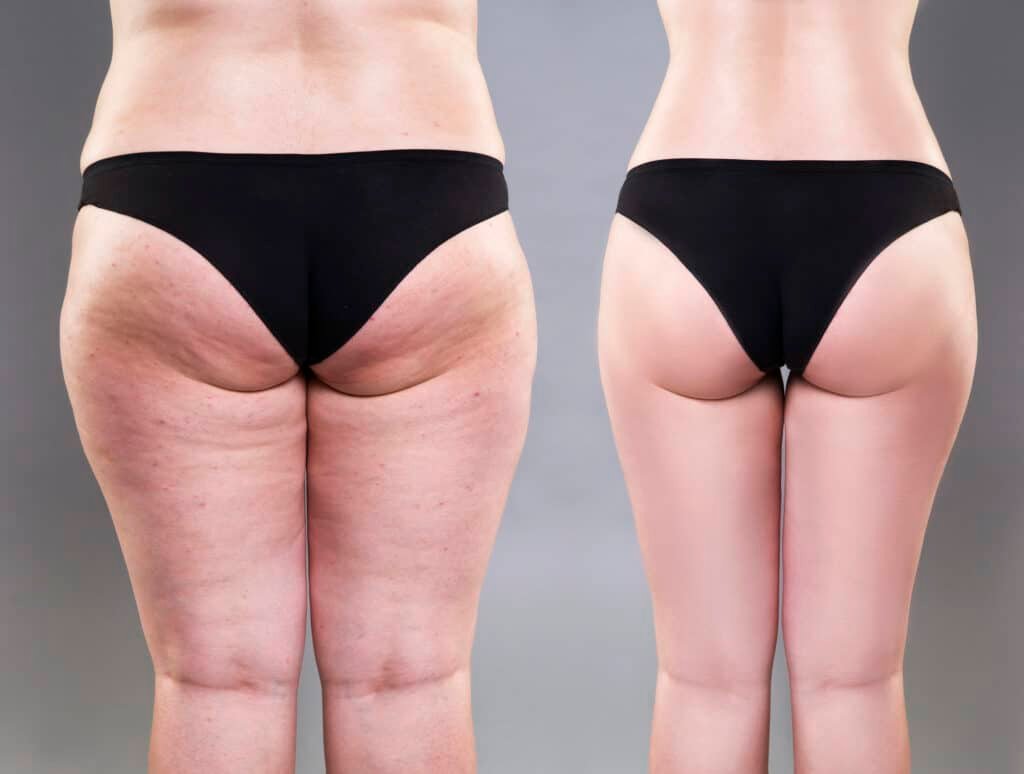
Cellulite is a common aesthetic issue that mainly affects women, regardless of age or body type. It is characterized by the appearance of irregularities in the texture of the skin. Cellulite is not necessarily related to body weight, but it can affect self-confidence and body image.
Causes of Cellulite
Cellulite is caused by the accumulation of fat and fluid between the skin and connective tissue. Some key factors contribute to its appearance:
- Genetic Predisposition: The structure of connective tissue and the tendency for fluid retention are hereditary.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in estrogen levels, especially during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, affect fat distribution and blood circulation.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of exercise reduces blood circulation and promotes fat accumulation.
- Poor Diet: Diets rich in sugar, salt, and fat promote fluid retention and inflammation.
- Stress: Elevated cortisol levels affect fat storage and microcirculation.
- Smoking and Pollution: They negatively affect microcirculation and collagen production.
Types and stages of cellulite
Forms of Cellulite
- Soft Cellulite: Occurs mainly in women with loose skin or insufficient muscle mass. It is more evident when the area is pressed.
- Compact Cellulite: More common in younger women or athletic individuals. The skin appears hard and is often accompanied by pain.
- Edema Cellulitis: Caused by fluid retention, mainly in the legs, and is associated with swelling.
Stages of Cellulite
- First Stage: Visible only with pressure on the skin.
- Second Stage: Visible when the person is sitting or standing.
- Stage Three: Visible even in a relaxed posture, with pronounced irregularities and dents.
Treatment Options
Cellulite treatment requires a combined approach, including professional methods, lifestyle improvements, and the use of specialized care products.
1. Non-Invasive Therapies
- Radio frequencies (RF): Stimulate lipolysis and collagen production, improving skin elasticity.
- Cryolipolysis: The application of cold reduces local fat and improves the texture of the area.
- Ultrasound (Cavitation): Breaks down fat cells while improving microcirculation.
- Pressotherapy: A method that enhances lymph circulation and reduces swelling.
- Intradermal Massage (LPG): Uses special devices to activate lymph and improve circulation.
2. Injectable Therapies
- Mesotherapy: Injectable solutions with lipolytic substances and vitamins that reduce fat and improve skin consistency.
- PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma): Improves skin quality and microcirculation.
Tips for preventing and managing cellulite
- Healthy Diet:
- Include fruits, vegetables, proteins, and foods rich in antioxidants.
- Limit salt and sugar, which cause fluid retention.
- Hydration: Drink enough water to improve microcirculation and eliminate toxins.
- Physical Activity:
- Do strengthening exercises to tone your muscles.
- Include aerobic activity to reduce fat.
- Skin Care:
- Use products with caffeine, retinol, or other ingredients that improve circulation.
- Get regular massages to stimulate lymph.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking reduces circulation and collagen production.
Conclusion
Cellulite can be difficult to completely eliminate, but there are many effective methods to improve the appearance of the skin. Preventing and managing cellulite requires a combination of treatments, a balanced diet, and exercise.




