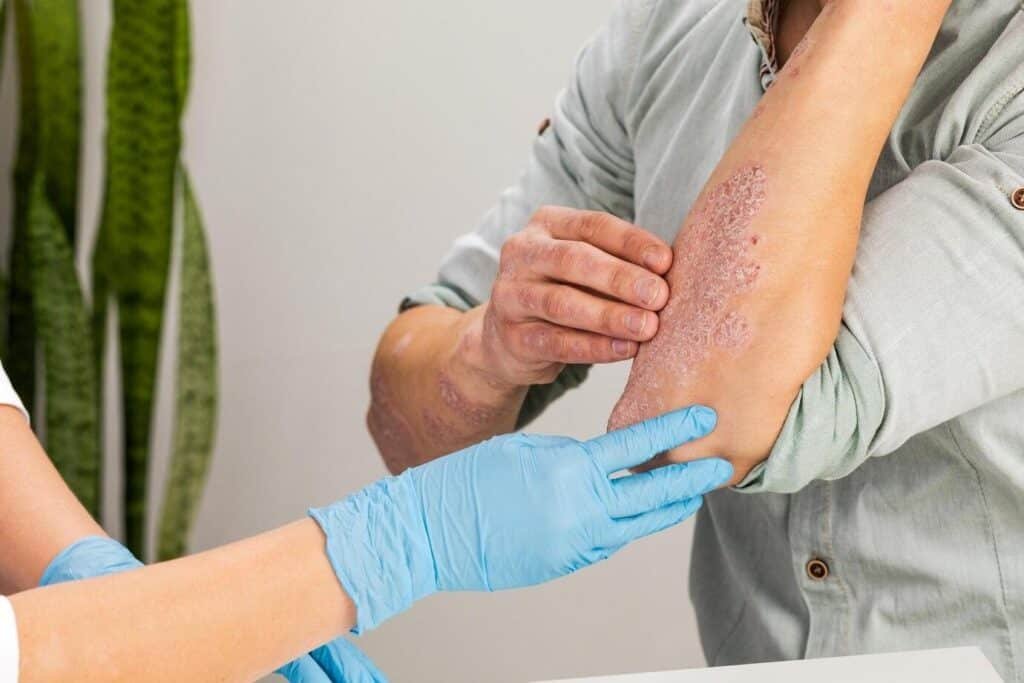
Psoriasis is a chronic, non-contagious skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is an autoimmune disorder that accelerates the turnover of skin cells, causing redness, scaling, and inflammation. Its exact cause is not clear, but factors such as heredity, stress, infections, and certain medications can make it worse.
Types of Psoriasis The condition manifests itself in various forms:
- Plaque psoriasis: Characterized by red plaques with white scales.
- Guttate psoriasis: Small, red spots that appear mainly in children and adolescents.
- Inverse psoriasis: Appears in skin folds, such as armpits and under the breasts.
- Pustular psoriasis: Rare, but serious form with white pustules filled with pus.
- Erythrodermic psoriasis: The most severe form, covering a large part of the body and requiring immediate medical attention.
Symptoms and Treatment Psoriasis is characterized by irritation, dryness, itching, and sometimes pain. Available treatments include topical creams, immunosuppressants, and biologic agents. In addition, lifestyle changes, a balanced diet, and avoidance of irritants help manage it.
Living with Psoriasis Although there is no definitive cure, modern approaches offer significant improvements in the quality of life of patients. Specialized care and proper information are key to controlling symptoms and maintaining healthy skin. If you notice symptoms, your dermatologist can guide you in the appropriate treatment.




